What (or who) really drives the FX market? Sure, it’s easy to think it’s all about you trading on MT4/MT5, getting rich, and showing off that Rolex on Instagram. But there’s more to it! In this article, we break down the roles of key participants in the foreign exchange market. By key participants, we mean other entities besides you, such as central banks, governments, sovereign wealth funds, professional trading firms, and retail traders. Central banks stabilize currencies, governments manage funding, and sovereign wealth funds make long-term investments that influence currency values. Meanwhile, trading firms enhance liquidity, and retail traders add speculative interest, each playing a unique part in this vast market. So, get yourself a cup of joe because we are about to begin.
What Are the Functions of the Forex Market?
Before we can move on to the core topic of our article—participants in the foreign exchange market—we will make a brief detour and discuss the functions of this market. Without having a handle on the functionality, our principal topic would be incomplete. Understanding functions gives context to why each participant is involved, what motivates their actions, and how they impact currency movements. So, bear with us.
Currency Exchange
Currency exchange plays a primary role. It allows an efficient conversion between currencies for individuals and organizations engaged in international trade or travel. Moreover, the forex market’s liquidity and efficiency empower companies to conduct cross-border transactions efficiently by ensuring quick access to currency and minimizing costs associated with the exchange, thereby strengthening the fabric of international trade.
Exchange Rate Determination
The forex market also determines exchange rates. It reflects the relative value of currencies, determined by the supply and demand dynamics within the forex market structure. Furthermore, the forex market ensures liquidity, which creates an environment where numerous buyers and sellers (often numbering in the millions globally) actively participate in currency trading. This liquidity enables easy entry and exit from positions and helps efficient price discovery within the forex market structure.
Risk Management
Risk management is essential in the forex market, as it offers players various tools and instruments to navigate foreign exchange risks effectively. By using currency derivatives such as futures and options, companies can hedge against adverse currency movements, protecting their financial interests. For example, a company might use a forward contract to lock in an exchange rate for a future transaction, mitigating the risk of adverse currency movements.
Speculation
Speculation and investment activities thrive within the forex market as traders and investors capitalize on their expectations of future currency movements, seeking profits through timely buy and sell decisions. For example, a trader might buy a currency pair when economic data suggests a strong future performance and sell it at a higher price once the market reacts positively to the news.
International Trade
As a facilitator of fund movement across borders, the forex market plays a pivotal role in financing international transactions, foreign investments, remittances, and other capital flows. It acts as a conduit for the efficient allocation of funds on a global scale, bolstering economic activity.
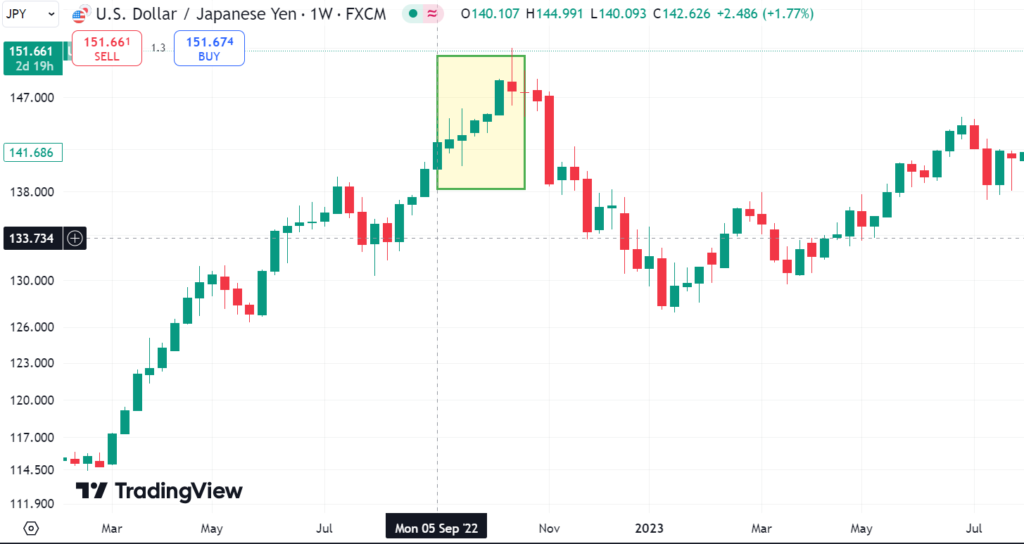
Central banks are by far the most important participants in the foreign exchange market as they wield substantial influence over their respective currencies. And not only because they print them. For example, in 2022, the Bank of Japan (BOJ) intervened (as shown in the image below) in the forex market to stabilize the yen, which was rapidly losing value against the US dollar. Notable interventions occurred in September and October as the yen fell to a 24-year low.
Source: TradingView
The BOJ’s primary objectives were to curb excessive yen depreciation, control inflation, and foster economic stability. The BOJ sold foreign reserves, specifically U.S. dollars, to achieve these goals. It also bought Japanese government bonds to help lower interest rates and support economic activity. Although these measures temporarily impacted the yen’s value, the overall trend of weakening continued due to the broader macroeconomic context, particularly the divergence in monetary policy between Japan and other countries, like the United States.
Who Are the Key Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market?
Many actors in the foreign exchange market have different goals and motives. We will place them into several categories to understand how the forex market works. As we pointed out in our previous article about What Moves the Foreign Exchange Market, the foreign exchange (FX) market is the largest financial market in the world. Central banks, large commercial banks, hedge funds, retail traders, and many other participants take part in this market daily. Let us review these key players in the forex market and their motivations to trade currencies.
Why Do Central Banks Take Part in the FX Market?
Sometimes, central banks step into the foreign exchange (FX) markets to influence their country’s exchange rate by adjusting its level or its trend over time. For instance, they might try to weaken their currency to boost exports, making their goods cheaper for buyers abroad. Other times, they work to strengthen the currency to fight inflation since a stronger currency makes imports less expensive.
Central banks tend to intervene mainly for two reasons: if they feel the currency is too weak or if the exchange rate drifts too far from a stable level—sometimes due to speculative trading. In these cases, central banks act as “market makers,” aiming to reduce the wild swings in the exchange rate that can disrupt trade and investment. Central banks rarely act alone, though—they often coordinate closely with their governments, which can blur the lines between them.
While central banks do have the power to influence exchange rates, they don’t have complete control. More considerable forces—like market dynamics, the economy’s underlying fundamentals, and global events—also play huge roles. Long-term interventions are often expensive and can deplete a country’s foreign reserves. Multiple central banks sometimes work together for a more significant impact, like during the 1985 Plaza Accord. The degree of transparency in these interventions varies a lot: some central banks openly announce their moves, while others operate more quietly.
IMPORTANT:
The Plaza Accord was an agreement signed on September 22, 1985, at the Plaza Hotel in New York City. It brought together five major countries—France, West Germany, Japan, the United Kingdom, and the United States—to work together to lower the U.S. dollar’s value. The goal was to depreciate the dollar relative to other key currencies, like the French franc, the German Deutsche Mark, the Japanese yen, and the British pound. They did this by intervening in currency markets to reduce the dollar’s value. After the agreement, the U.S. dollar fell significantly, and this continued until the Louvre Accord replaced the Plaza Accord in 1987. Some experts even argue that the Plaza Accord contributed to creating the asset price bubble in Japan during the late 1980s. (Source)
Another way central banks influence exchange rates is through monetary policy, especially by setting interest rates. Higher interest rates generally attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the currency and making it appreciate. To counter the effect of these interventions on the domestic money supply, central banks often use “sterilization.” For example, if they sell foreign currency to weaken their own, they might simultaneously sell government bonds to absorb the extra domestic money.
Sometimes, though, a central bank will act when it believes its currency is too strong. A stronger currency can hurt export competitiveness by making domestic goods more expensive for foreign buyers, which can reduce demand. An excellent example of this is the Swiss National Bank’s efforts to weaken the Swiss franc against the euro, which it did by selling Swiss francs in 2010, 2013, and again in 2015.
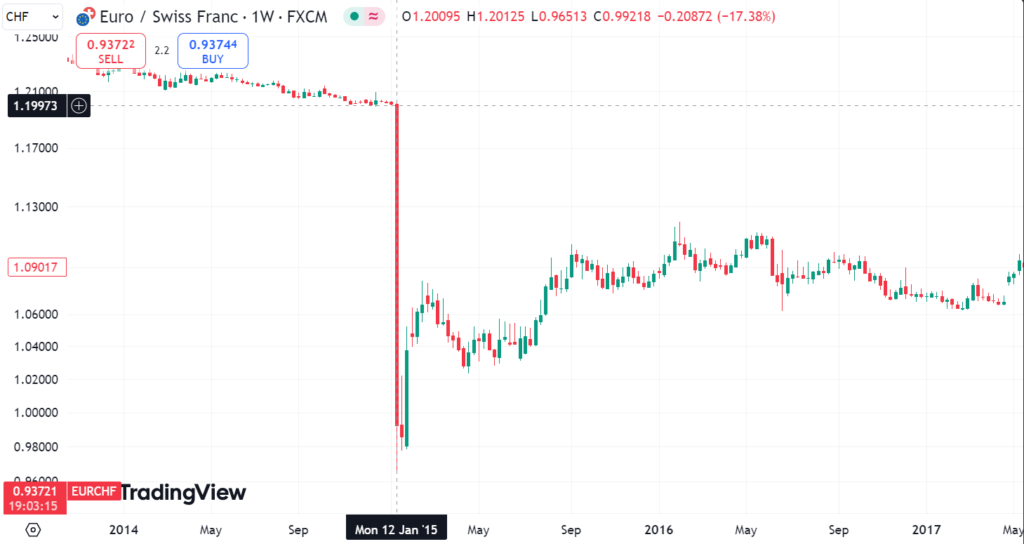
Source: TradingView. On January 15, 2015, the SNB shocked markets by abruptly abandoning the euro-franc peg they had maintained since 2011.
Why Do Governments Participate in the Foreign Exchange Market?
Governments are some of the biggest participants in the foreign exchange market, using it for a wide range of needs, from funding embassies around the world to covering massive military contracts. Their moves in the FX market can have a real impact on exchange rates and global money flows.
The U.S. Department of State’s FY 2023 budget for ESCM (Embassy Security, Construction, and Maintenance) was listed as approximately $1.95 billion in resources directed toward embassy construction, maintenance, and security enhancements.
A 2014 study by the Cato Institute estimated the annual cost of maintaining US military bases worldwide to be around $55 billion. This includes operational costs, personnel expenses, and construction.
The FX market helps governments reach different policy goals. For instance, they manage foreign currency reserves to keep their own currency stable and meet obligations with other countries. By buying or selling currencies, governments can also influence the value of their own currency to make exports more appealing or keep import costs in check. Sometimes, they even use the market to hedge against risk or, on rare occasions, for speculative purposes.
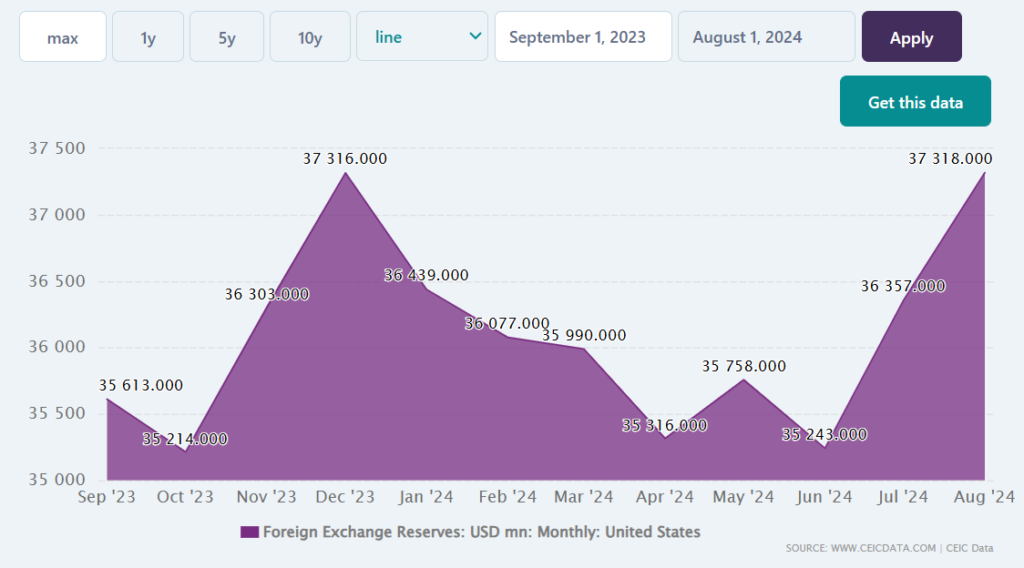
United States’s Foreign Exchange Reserves from Sep 2023 to Aug 2024
Government involvement in the FX market isn’t just limited to central banks. It can include treasury departments or sovereign wealth funds too, showing just how varied their role is. All in all, governments play a crucial role in the FX market, with their decisions shaped by a mix of economic goals and political strategies.
Why Do SWFs (Sovereign Wealth Funds) Participate in the FX Market?
Another key player is Sovereign Wealth Funds or SWFs for short. SWFs are organizations closely related to the public sector. Very often, countries running current account surplus (a country exports more goods and services than imports) through SWFs invest some of these funds in financial assets such as stocks, bonds, hedge funds, real estate, etc. For example, Norway’s SWF (total market value in USD, as of July 2024, $1,666,580,078,125) has invested in major technology companies like Apple (1.14% of the entire portfolio as of 2024) and Microsoft (1.28% of the whole portfolio) among other assets.
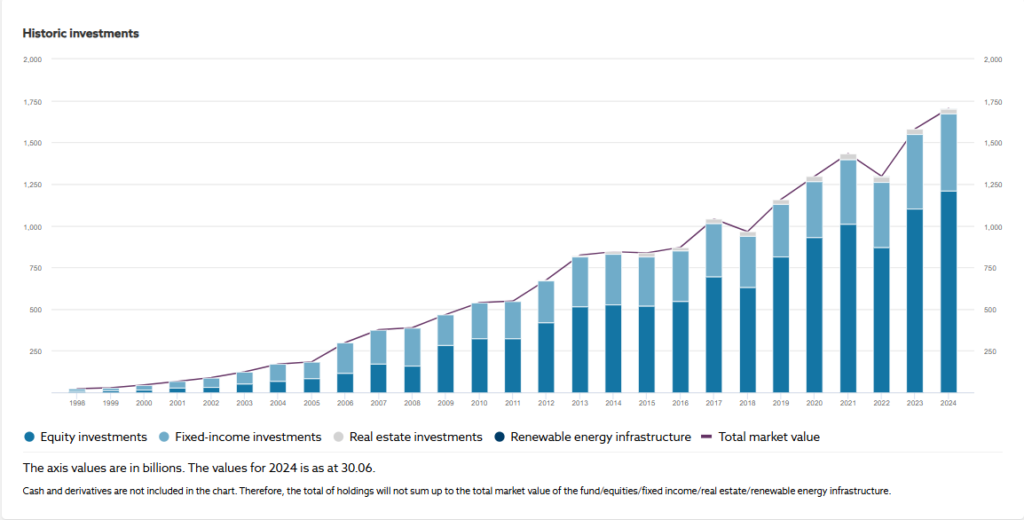
Source: https://www.nbim.no/en/the-fund/investments/#/2024/investments/equities
Countries like China, Norway, the United Arab Emirates, and Kuwait are some of the largest SWFs in the world. Given their size, it is only natural they can significantly impact almost all exchange rates. However, their influence is generally less direct than central banks or large commercial banks, as they focus on long-term investments rather than short-term trading that moves markets.
Why Do Professional Trading Firms Take Part in the FX Market?
Almost any firm that professionally manages foreign exchange risk for profit can be considered a professional trading firm. For example, high-frequency algorithmic traders, hedge funds, and prop firms (don’t confuse these entities with those that run “competitions” for retail traders) can be counted as such. This bucket of key players accounts for a growing volume of daily foreign exchange transactions.
Professional trading firms actively participate in the FX market for profit generation, liquidity provision, risk management, arbitrage opportunities, portfolio diversification, and advanced trading technologies. They capitalize on price movements, analyze trends, and employ advanced strategies. By providing liquidity, they enhance market efficiency.
For example, many professional trading firms use high-frequency (HF) algorithmic systems to ensure rapid transactions and tighter bid-ask spreads. The major HF firms in the U.S. are Virtu Financial, Tower Research Capital, Tradebot, and Citadel LLC. They protect portfolios by hedging and managing risks, seeking arbitrage opportunities, and exploiting price inefficiencies. They diversify portfolios by accessing various markets, leveraging advanced technologies, and executing trades swiftly. Overall, their involvement contributes to the functioning and liquidity of the forex market.
STATS:
Regarding the global FX market, the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) conducts a comprehensive global foreign exchange market survey every three years. Their April 2022 survey revealed an average daily turnover of $7.5 trillion in the global FX market. While the survey doesn’t isolate trading volume from professional trading firms specifically, it provides a valuable benchmark. A significant portion of this volume (48%) is attributed to “other financial institutions,” which includes entities like non-reporting banks, hedge funds, and proprietary trading firms (PTFs), amounting to approximately $3.6 trillion per day. On the other hand, the Federal Reserve Bank of New York’s Foreign Exchange Committee also conducts semi-annual North American FX volume surveys. Their April 2024 survey indicated an average daily volume in over-the-counter (OTC) FX instruments of $1,165.2 billion. Though it doesn’t break down volume by firm type, this survey offers insight into regional FX trading activity.
Retailers Are the Smallest Participants in the Foreign Exchange Market
Retail traders participate in currency trading for various purposes, including personal travel, online shopping, and speculative investments. Thanks to advances in electronic trading technology, retail traders can now speculate on exchange rate movements and even move their savings into foreign currencies using electronic trading platforms, such as MetaTrader, TradingView, cTrader, etc.
A wide range of currency pairs is usually available, including major currencies like the USD, EUR, and JPY and exotic currency pairs. Therefore, retail traders can actively trade currency pairs using these platforms from anywhere at any time. However, it may come as a surprise that these online trading platforms, provided by brokers (technically, they are considered dealers), don’t grant retail traders direct access to the forex market. It is neither a bad nor a good thing. It is just a fact of life. Given the size and structure of the forex market, retail traders do not play a significant role in the grand scheme of things. We wrote a detailed article on this topic. If you are interested, you can access it here.
Retail traders usually operate with a smaller capital and may have limited knowledge and experience compared to professional investors or trading firms. However, they still contribute to the overall forex market structure. They make trading decisions based on technical analysis, fundamental analysis, or trading signals.
STATS:
It’s important to note that retail FX transaction volumes are generally smaller than institutional trades. For instance, institutional trades can account for over 90% of daily forex volume, while retail trades make up a much smaller portion. According to the Triennial Central Bank Survey, as of 2016, retail foreign exchange trading represented 5.5% of the whole foreign exchange market ($282 billion in daily trading turnover). A lot of time has passed since then, and we can safely assume that this number has increased. Even so, this is just a drop in the ocean compared to other participants in the foreign exchange market.
Conclusions
In conclusion, understanding the functions and key participants in the foreign exchange market gives you, the trader or investor, a valuable foundation to navigate the FX market effectively. Recognize the tangible forces at play rather than subscribing to myths about shadowy figures or secret algorithms controlling prices. Central banks, governments, sovereign wealth funds, and trading firms are the true market movers with clear motives, using the market’s mechanisms to achieve objectives like currency stabilization, liquidity, and risk management.
By grasping these fundamentals, you can make more informed trading decisions, align with real market dynamics, and shift from speculation to a strategy grounded in the realities of the FX landscape. We hope this insight equips you to approach forex confidently, grounded in facts, and ready to participate in the world’s largest financial market. Our industry is full of misconceptions, and if this article helps someone transition into the world of genuine science and facts, we’ll be glad to have been part of that journey.